BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is the essential firmware that acts as the communication bridge between your computer’s hardware and operating system. Think of it as your computer’s “startup manager” that initializes all hardware components before Windows 11 or any other operating system takes control.
BIOS Full Form & Functions
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System and performs four critical functions:
- Power-On Self Test (POST) – Checks hardware functionality at startup
- Bootstrap Loader – Locates and loads your operating system
- Hardware Drivers – Manages communication between OS and hardware
- CMOS Setup – Provides configuration interface for system settings
Transition to UEFI BIOS
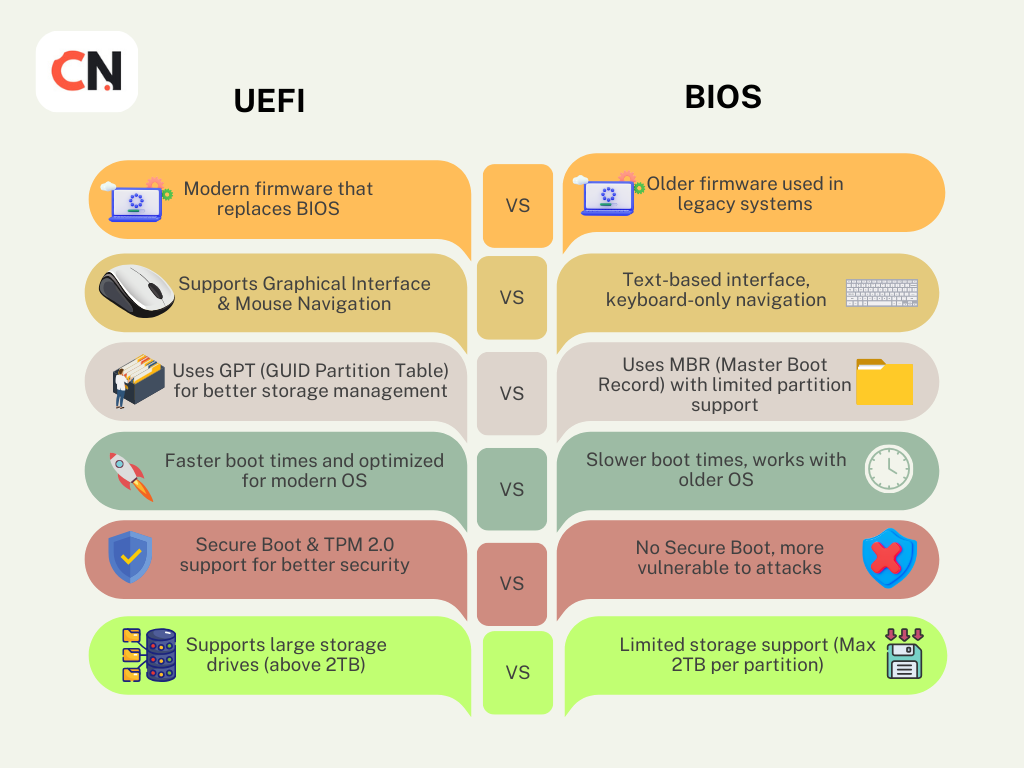
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the modern replacement for traditional BIOS. It offers:
- Support for 64-bit architectures
- Faster boot times with optimized hardware initialization
- Secure Boot to prevent malware execution during startup
- Graphical user interfaces for easier configuration
- Support for larger hard drives (beyond 2TB) with GPT partitioning
How to Enter BIOS
Universal BIOS Keys by Brand
Knowing how to open BIOS depends on your computer manufacturer. Here’s the complete BIOS key reference:
Desktop Motherboards:
- ASUS BIOS: F2 or Delete key
- MSI BIOS: Delete key (some models: F2)
- Gigabyte: Delete key
- ASRock: F2 or Delete key
- EVGA: Delete key
Laptop Manufacturers:
- ASUS: F2 key during startup
- MSI: Delete or F2 key
- HP BIOS: F10 or Esc key
- Dell BIOS: F2 or F12 key
- Lenovo BIOS: F2 or Fn+F2 (ThinkPads)
- Acer: F2 or Delete key
How to Boot to BIOS (Step-by-Step)
Method 1: Traditional Startup Method
- Restart your computer completely
- Watch for manufacturer logo screen
- Press the designated BIOS key repeatedly
- Continue pressing until BIOS interface appears
Method 2: Windows 11 Advanced Startup For fast-booting systems where traditional method doesn’t work:
- Hold Shift while clicking “Restart” in Windows 11
- Select “Troubleshoot” → “Advanced Options”
- Choose “UEFI Firmware Settings”
- Click “Restart” to boot directly to BIOS
Method 3: Settings App (Windows 11)
- Open Windows 11 Settings (Win + I)
- Go to “Update & Security” → “Recovery”
- Under “Advanced startup,” click “Restart now”
- Follow Method 2 steps above
How to Update BIOS
BIOS update is crucial for security, performance, and hardware compatibility.
Here’s why and how to do it safely:
Why Update BIOS?
- Security patches for firmware vulnerabilities
- Hardware compatibility for new components
- Performance improvements and bug fixes
- Windows 11 TPM requirements support
Pre-Update Safety Checklist
CRITICAL: Never interrupt a BIOS update process
- Check current BIOS version: Press Win+R, type
msinfo32 - Backup important data (precautionary)
- Ensure stable power (use UPS if available)
- Close all programs and disable antivirus temporarily
- Charge laptop battery to minimum 50%
Brand-Specific BIOS Instructions
ASUS BIOS Update
Method 1: ASUS AI Suite (Recommended)
- Download ASUS AI Suite from official website
- Install and restart your computer
- Launch AI Suite → BIOS Update section
- Let software automatically detect updates
- Follow installation prompts (never power off during update)
Method 2: EZ Flash Utility
- Download .CAP BIOS file from ASUS support
- Format USB drive to FAT32
- Copy BIOS file to USB root directory
- Enter BIOS (F2/Delete) → Tool → ASUS EZ Flash 3
- Select USB drive and BIOS file
Method 3: BIOS Flashback For motherboards with Flashback button:
- Rename BIOS file per motherboard specifications
- Copy to FAT32 USB drive
- Insert into designated Flashback port
- Power off system, press Flashback button 3 seconds
- Wait for LED completion indicator
MSI BIOS Update
Method 1: MSI Center
- Install MSI Center from official website
- Navigate to Support → LIVE UPDATE
- Scan for available BIOS updates
- Download and install automatically
- Restart when prompted
Method 2: M-Flash Utility
- Download BIOS .zip file from MSI support
- Extract to FAT32 USB drive
- Enter BIOS (Delete key) → M-FLASH
- Select “Update BIOS and ME”
- Choose USB drive and BIOS file
Gigabyte BIOS Update
Method 1: @BIOS Utility
- Download @BIOS from Gigabyte website
- Run as administrator
- Click “Update BIOS from Gigabyte Server”
- Auto-detect motherboard and update
- Wait for completion
Method 2: Q-Flash
- Download BIOS file to FAT32 USB
- Enter BIOS (Delete) → Press F8 for Q-Flash
- Select “Update BIOS” → Choose USB drive
- Select BIOS file and confirm
HP BIOS Update
Method 1: HP Support Assistant
- Install HP Support Assistant
- Launch → Updates tab
- Scan for BIOS updates automatically
- Download and install if available
- Restart to complete
Method 2: Manual Download
- Visit HP Support → Enter model number
- Download latest BIOS .exe file
- Run as administrator
- Follow HP BIOS Update Utility
- Do not power off during process
Dell BIOS Update
Method 1: Dell SupportAssist
- Install Dell SupportAssist
- Click “Get Started” → “Check for Updates”
- Install available BIOS updates
- Follow on-screen instructions
- Restart when prompted
Method 2: Manual Process
- Visit Dell Support → Enter service tag
- Go to Drivers & Downloads → Filter by BIOS
- Download latest update executable
- Run as administrator
- Follow Dell BIOS Flash Utility
Lenovo BIOS Update
Method 1: Lenovo Vantage
- Install Lenovo Vantage from Microsoft Store
- Open Device Settings → System Update
- Scan for BIOS updates automatically
- Download and install if available
- Restart to complete update
Method 2: ThinkPad BIOS Update Utility
- Download ThinkPad BIOS Update Utility
- Run utility to detect current version
- Download and install latest version
- Restart ThinkPad to complete
Note: For detailed step-by-step BIOS update procedures with safety tips, check our comprehensive guide on BIOS updates for all major brands
BIOS Settings Explained
Essential BIOS Settings Every User Should Know
Boot Settings:
- Boot Priority/Order: Controls which device boots first
- Fast Boot: Enables/disables quick startup
- Secure Boot: Security feature for Windows 11
- CSM Support: Legacy compatibility mode
Hardware Configuration:
- SATA Mode: AHCI vs IDE for storage drives
- Virtualization: Intel VT-x/AMD-V for virtual machines
- USB Configuration: Enable/disable USB ports
- Integrated Graphics: Control onboard video
Performance Settings:
- CPU Settings: Overclocking and power management
- Memory Settings: RAM frequency and timings
- Fan Control: Temperature and noise management
- Power Management: Sleep states and wake options
How to Tell What Motherboard I Have
Method 1: System Information
- Press Win+R, type
msinfo32 - Look for “BaseBoard Product” and “BaseBoard Manufacturer”
Method 2: Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt as administrator
- Type:
wmic baseboard get product,manufacturer,version,serialnumber
Method 3: CPU-Z Software
- Download and install CPU-Z
- Go to “Mainboard” tab
- View complete motherboard information
Method 4: Physical Inspection
- Look for model number printed on motherboard
- Usually located near CPU socket or RAM slots
Gaming & Emulation BIOS
PS2 BIOS for PCSX2 Emulator
What is PS2 BIOS? PS2 BIOS files are required for PCSX2 emulator to run PlayStation 2 games on PC. These are system files from original PS2 console.
Legal Way to Obtain PS2 BIOS:
- Own an original PlayStation 2 console
- Use homebrew software to extract BIOS
- Transfer files to your PC for emulator use
PCSX2 BIOS Setup:
- Download and install PCSX2 emulator
- Run initial setup wizard
- Browse to your legally obtained BIOS files
- Select appropriate region BIOS (USA, PAL, Japan)
- Complete configuration for gaming
PS1 BIOS for PlayStation Emulation
PS1 BIOS Requirements: Similar to PS2, PS1 BIOS files are needed for PlayStation 1 emulation using software like ePSXe or DuckStation.
Setup Process:
- Obtain BIOS legally from owned PS1 console
- Place BIOS files in emulator directory
- Configure emulator to recognize BIOS
- Test with compatible game ROM
Important Note: Always use BIOS files from consoles you legally own. Downloading copyrighted BIOS files is illegal.
Advanced Tools and Utilities
HWMonitor – System Monitoring
HWMonitor is essential software for monitoring system temperatures, voltages, and fan speeds – crucial when tweaking BIOS settings.
Key Features:
- Real-time temperature monitoring
- CPU, GPU, and motherboard sensor readings
- Fan speed monitoring
- Voltage level tracking
- Compatible with all major hardware brands
When to Use HWMonitor:
- After BIOS updates to verify system stability
- When overclocking CPU or memory
- Monitoring temperatures during stress testing
- Checking fan curves and thermal performance
Balena Etcher – USB Creation Tool
Balena Etcher helps create bootable USB drives for BIOS updates and system recovery.
Uses for BIOS Management:
- Creating DOS boot USB for BIOS updates
- Making recovery drives for BIOS restoration
- Burning ISO images for system diagnostics
- Preparing bootable media for firmware updates
Troubleshooting Common BIOS Issues
System Won’t Boot After BIOS Update
Immediate Solutions:
- Clear CMOS: Remove CMOS battery for 10 minutes
- BIOS Recovery: Use manufacturer recovery features
- Dual BIOS: Switch to backup BIOS (if available)
- Contact Support: Manufacturer technical support
Prevention Tips:
- Always use correct BIOS file for exact motherboard model
- Ensure stable power during update process
- Never interrupt BIOS update procedure
- Keep backup of working BIOS when possible
BIOS Settings Reset
Common Causes:
- CMOS battery failure
- Power surges or outages
- Hardware changes
- Firmware updates
Solutions:
- Replace CMOS battery (CR2032)
- Reconfigure essential settings
- Load optimized defaults
- Update BIOS to latest version
Hardware Not Detected
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check physical connections
- Enable device in BIOS settings
- Update BIOS for hardware compatibility
- Verify power supply adequacy
- Test hardware in another system
BIOS Security and Best Practices
Windows 11 BIOS Requirements
Essential Settings for Windows 11:
- TPM 2.0: Trusted Platform Module enabled
- Secure Boot: Must be enabled
- UEFI Mode: Legacy/CSM disabled
- CPU Virtualization: Intel VT-x/AMD-V enabled
Checking Windows 11 Compatibility:
- Press Win+R, type
tpm.msc - Verify TPM 2.0 is present and enabled
- Run PC Health Check tool from Microsoft
- Enable required BIOS settings if missing
BIOS Security Features
Important Security Settings:
- Administrator Password: Prevents unauthorized changes
- Boot Password: Required to start system
- Secure Boot: Prevents malware during startup
- Intel TXT/AMD HVCI: Hardware-based security
Security Best Practices:
- Keep BIOS updated with latest security patches
- Enable password protection for BIOS access
- Use Secure Boot when supported
- Regular firmware security audits
Performance Optimization
Best BIOS Settings for Gaming
CPU Optimization:
- Enable all CPU cores and hyperthreading
- Set CPU to performance/high performance mode
- Disable C-states for consistent performance
- Enable CPU virtualization for modern games
- Set CPU fan curves for optimal cooling
- Disable CPU throttling unless necessary
Memory Optimization:
- Enable XMP/DOCP profiles for rated RAM speeds
- Set optimal memory frequency (3200MHz+ for modern systems)
- Adjust memory timings for stability vs performance
- Enable memory training for better compatibility
- Set memory voltage to manufacturer specifications
- Configure memory channels properly
Graphics Settings:
- Set PCIe slot to Gen 3/4 for dedicated GPU
- Enable Resizable BAR/Smart Access Memory (AMD/Intel)
- Disable integrated graphics when using dedicated GPU
- Optimize PCIe lane distribution for multi-GPU setups
- Enable Above 4G Decoding for high-end GPUs
- Set primary display adapter correctly
Storage Optimization:
- Enable AHCI mode for SSDs
- Configure NVMe drives in PCIe mode
- Enable hot-swapping if needed
- Set optimal SATA port configuration
- Enable TRIM support for SSDs
Overclocking Basics
Safe Overclocking Approach:
- Research your specific CPU/GPU limits
- Start with small 100MHz increments
- Monitor temperatures closely (under 80°C for CPU)
- Test stability with stress tests for 24+ hours
- Document all stable settings and voltages
- Have CMOS reset procedure ready
- Keep backup of working configurations
Essential Monitoring Tools:
- HWMonitor: Real-time temperature and voltage monitoring
- Prime95: CPU stress testing and stability verification
- FurMark: GPU stress testing and thermal monitoring
- MemTest86: Memory stability and error checking
- Crystal Disk Mark: Storage performance benchmarking
Advanced Performance Tips:
- Disable unnecessary startup services in BIOS
- Enable Intel Turbo Boost or AMD Precision Boost
- Configure power delivery settings for stability
- Optimize fan curves for noise vs cooling balance
- Set custom voltage curves for efficiency
Content Creator & Professional Workstation Setup
Video Editing & Rendering Optimization
CPU Settings for Content Creation:
- Enable all available CPU cores and threads
- Set CPU to maximum performance mode
- Configure Intel Quick Sync or AMD VCE
- Enable hardware acceleration features
- Optimize CPU cache settings
Memory Configuration:
- Install maximum supported RAM (32GB+ recommended)
- Enable fastest supported memory speeds
- Configure dual-channel or quad-channel properly
- Set appropriate memory timings for stability
- Enable ECC memory if supported
Storage Configuration:
- Set NVMe drives for OS and active projects
- Configure RAID arrays for backup storage
- Enable AHCI mode for all SATA devices
- Optimize storage controller settings
- Configure scratch disk priorities
Streaming & Live Broadcasting Setup
Essential BIOS Settings for Streamers:
- Enable Intel Quick Sync Video for hardware encoding
- Configure GPU scheduling for dual-GPU setups
- Enable USB 3.0+ for high-quality capture devices
- Optimize PCIe lane allocation for capture cards
- Configure audio codec settings for low latency
Network and Connectivity:
- Enable Wake-on-LAN for remote management
- Configure onboard Ethernet for stable streaming
- Enable USB fast charging for mobile devices
- Set up multiple monitor support in BIOS
- Configure Thunderbolt/USB-C settings
Enterprise & Business Workstation Configuration
Security-Focused BIOS Setup
Corporate Security Requirements:
- Enable TPM 2.0 for BitLocker encryption
- Configure Secure Boot with custom certificates
- Enable Intel TXT or AMD Memory Guard
- Set up BIOS administrator passwords
- Configure boot device restrictions
- Enable hardware-based malware protection
Remote Management Setup:
- Enable Intel vPro or AMD PRO features
- Configure IPMI for server management
- Set up Wake-on-LAN for remote access
- Enable network boot options (PXE)
- Configure SNMP for monitoring
- Set up automatic BIOS update policies
Compliance & Audit Features:
- Enable BIOS event logging
- Configure hardware asset reporting
- Set up compliance monitoring
- Enable secure firmware verification
- Configure audit trail settings
Specialized Hardware Configuration
Multi-GPU Gaming & AI Workstations
NVIDIA SLI Configuration:
- Enable SLI in BIOS settings
- Set PCIe slots to appropriate speeds
- Configure power delivery for multiple GPUs
- Enable Above 4G Decoding
- Set primary display adapter
- Configure SLI bridge detection
AMD CrossFire Setup:
- Enable CrossFire support in BIOS
- Configure PCIe lane distribution
- Set optimal power management
- Enable CrossFire bridge detection
- Configure display output priorities
AI/Machine Learning Optimization:
- Enable maximum PCIe lanes for GPUs
- Configure large memory support (>128GB)
- Enable ECC memory if available
- Set CPU affinity for NUMA systems
- Configure power delivery for sustained loads
- Enable hardware virtualization features
Mining & Cryptocurrency Configuration
Mining-Specific BIOS Settings:
- Enable mining mode (if available)
- Set PCIe slots to Gen2 for stability
- Configure multiple GPU detection
- Enable Above 4G Decoding
- Set power management for efficiency
- Configure automatic restart features
Important Mining Considerations:
- Set appropriate power limits
- Configure temperature monitoring
- Enable automatic fan control
- Set up power failure recovery
- Configure BIOS watchdog timers
- Enable remote monitoring capabilities
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I update my BIOS?
Only when necessary – for security patches, hardware compatibility issues, or specific problems.
Don’t update just because newer version exists.
Rule of thumb: if your system is working fine, only update for security reasons.
Can BIOS updates improve performance?
Yes, especially for memory compatibility, CPU microcode updates, and hardware optimization. Updates can improve RAM speeds, fix CPU vulnerabilities, and enhance overclocking capabilities. However, performance gains are usually modest (1-5%).
What’s the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
UEFI is the modern replacement for BIOS, offering faster boot times (often 30-50% faster), better security (Secure Boot), graphical interface, support for drives larger than 2TB, and mouse support in setup.
Is it safe to update BIOS on laptop?
Yes, but ensure laptop is plugged in and battery is charged above 50%. Use manufacturer’s official update tools only. Laptop BIOS updates often include critical thermal management and power optimization improvements.
Can I downgrade BIOS to older version?
Usually possible, but some motherboards prevent downgrading for security reasons. Gaming motherboards typically allow downgrades, while business/enterprise boards may restrict this. Always check manufacturer documentation.
Why does my computer boot slower after BIOS update?
New BIOS may include additional hardware checks, security features, or memory training. You can often optimize boot settings: disable full memory test, enable fast boot, reduce POST delay, skip floppy drive detection.
What if my computer boots too fast to press BIOS key?
Use Windows 11 Advanced Startup: Hold Shift while clicking Restart → Troubleshoot → Advanced Options → UEFI Firmware Settings. Alternatively, disable Fast Startup in Windows Power Options.
Which BIOS key should I press if multiple keys are listed?
Try Delete key first (most common), then F2. For laptops, try F2 first. If unsure, press multiple keys rapidly during startup. Some systems show “Press [key] to enter setup” message.
How do I know if my system uses BIOS or UEFI?
Press Win+R, type “msinfo32”. If you see “BIOS Mode: UEFI”, you have UEFI. If it shows “Legacy”, you have traditional BIOS. UEFI systems typically have graphical interfaces with mouse support.
Can I use mouse in BIOS?
Only in UEFI systems. Traditional BIOS requires keyboard navigation only. UEFI interfaces support mouse, touch screens, and have modern graphical layouts.
What does “BIOS password” protect?
BIOS/Setup password prevents unauthorized access to BIOS settings. Boot password requires password before system starts. HDD password locks hard drive data. Each serves different security purposes.
How do I know if my BIOS update was successful?
Check system information (msinfo32) to verify new BIOS version. System should boot normally with all hardware detected. Monitor system stability for 24-48 hours after update.
Will BIOS update fix my hardware compatibility issues?
Often yes. BIOS updates frequently include memory compatibility improvements, CPU microcode updates, GPU support enhancements, and USB device compatibility fixes. Check update changelog for specific fixes.
Can BIOS updates add support for new CPUs?
Yes, especially for AM4 (AMD) and LGA 1151/1200 (Intel) sockets. Many motherboards gained support for newer CPU generations through BIOS updates. Always check CPU support list before upgrading processor.
Why isn’t my new RAM running at rated speed?
Enable XMP (Intel) or DOCP (AMD) profiles in BIOS. If profiles aren’t available, manually set memory frequency and timings. Some older motherboards require BIOS updates for faster RAM support.
How do I enable TPM for Windows 11?
Enter BIOS → Security settings → Enable TPM 2.0 or Platform Trust Technology (PTT). Location varies by manufacturer: ASUS (Advanced → PCH-FW Configuration), MSI (Security → Trusted Computing), Gigabyte (Peripherals → Trusted Computing).
What happens if power fails during BIOS update?
Can potentially brick motherboard, but many modern boards have recovery features: BIOS Flashback (ASUS), BIOS Recovery (MSI), Q-Flash Plus (Gigabyte), or Dual BIOS systems. Always use UPS for BIOS updates.
How do I recover from bad BIOS update?
Try these methods in order: 1) Clear CMOS (remove battery 10 minutes), 2) Use BIOS Flashback button, 3) Dual BIOS recovery, 4) Contact manufacturer support, 5) Professional motherboard repair service.
Why did my BIOS settings reset?
Common causes: CMOS battery failure (CR2032), power surges, hardware changes, or BIOS updates. Replace CMOS battery every 3-5 years. Use UPS to prevent power-related resets.
Computer won’t start after changing BIOS settings – what to do?
) Clear CMOS (remove power, press CMOS clear button or remove battery), 2) Try different RAM slots, 3) Remove all USB devices, 4) Reset to optimized defaults, 5) Update BIOS if accessible.
How do I backup my BIOS settings?
Modern UEFI systems: Use “Save User Defaults” or “Save Profile” options. Take photos of important settings pages. Some motherboards allow exporting settings to USB drive. Document overclock settings separately.
Do I need special BIOS settings for gaming?
Enable: XMP/DOCP for RAM, CPU Turbo Boost, GPU overclocking, Resizable BAR, all CPU cores. Disable: C-states (for consistent performance), integrated graphics (if using dedicated GPU), unnecessary USB devices.
How do I enable Resizable BAR for better gaming performance?
Requirements: RTX 30-series or RX 6000-series GPU, compatible CPU/motherboard. Enable in BIOS: Above 4G Decoding → Enable, Resizable BAR Support → Enable. Update GPU drivers and verify activation in GPU software.
Should I disable hyperthreading for gaming?
Generally no. Modern games benefit from hyperthreading. Only disable for competitive esports where frame consistency matters more than peak performance, or if you experience stuttering in specific games.
How do I optimize BIOS for VR gaming?
Enable: USB 3.0+ ports, maximum CPU performance, XMP memory profiles, dedicated graphics, fast boot. Disable: power saving features, CPU parking, integrated graphics. Ensure stable power delivery settings.
Where do I legally get PS2 BIOS for PCSX2?
Extract from your owned PlayStation 2 console using homebrew software. Never download BIOS files from internet – this violates copyright. Popular extraction tools: Free McBoot, uLaunchELF, PS2 Independence Exploit.
Which PS2 BIOS version is best for PCSX2?
Use BIOS matching your game region: SCPH-70012 (USA), SCPH-70002 (Europe), SCPH-70000 (Japan). Newer BIOS versions (700xx series) generally offer better compatibility than older ones.
Can I use PS1 BIOS for PS2 games?
No, PS2 games require PS2 BIOS. PS1 BIOS only works for PlayStation 1 games in emulators like ePSXe, DuckStation, or Mednafen. Different console generations need their respective BIOS files.
How do I set up PCSX2 BIOS correctly?
1) Obtain legal BIOS files, 2) Place in PCSX2/bios folder, 3) Run PCSX2 setup wizard, 4) Browse to BIOS folder, 5) Select appropriate region BIOS, 6) Configure controller and graphics settings.
What is CSM and should I enable it?
Compatibility Support Module enables legacy BIOS boot mode. Disable for Windows 11 and modern OS installations. Enable only if using very old operating systems or specific legacy hardware/software requirements.
How do I enable virtualization in BIOS?
Intel: Enable “Intel VT-x” or “Intel Virtualization Technology”. AMD: Enable “AMD-V” or “SVM Mode”. Usually found in CPU Configuration, Advanced, or Security sections. Required for VMware, VirtualBox, Hyper-V.
What’s the difference between AHCI and IDE mode?
AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) enables modern features like Native Command Queuing, hot swapping, faster speeds. IDE mode provides legacy compatibility but limits performance. Always use AHCI for modern systems.
Should I enable Intel Management Engine (ME)?
For most users, yes. ME provides security features, remote management, and hardware functionality. Disable only if you have specific security/privacy concerns and understand the functionality loss.
How do I configure dual monitors in BIOS?
Enable: Primary Graphics Adapter (PCIe/Integrated), Multi-Monitor Support, Integrated Graphics (if using hybrid setup). Configure display priorities and assign displays to appropriate graphics outputs.
How do I identify my exact motherboard model?
Methods:
1) System Information (msinfo32),
2) Command prompt: “wmic baseboard get product,manufacturer”,
3) CPU-Z software,
4) Physical inspection of motherboard,
5) Original purchase documentation.
Are BIOS updates different for OEM vs custom PCs?
Yes. OEM systems (Dell, HP, Lenovo) use manufacturer-specific BIOS with custom features and restrictions. Custom PCs use motherboard manufacturer’s standard BIOS. Always use appropriate update tools for your system type.
Can I use ASUS BIOS file on MSI motherboard?
Absolutely not. BIOS files are specific to exact motherboard models and manufacturers. Using wrong BIOS will brick your motherboard. Always verify exact model number and revision before updating.
What’s the difference between Beta and Stable BIOS?
Stable/Final BIOS: Thoroughly tested, recommended for most users. Beta BIOS: Latest features but potentially unstable, use only if you need specific fixes or features and can handle potential issues.
How do I check my motherboard’s BIOS update history?
Visit manufacturer’s support page, enter motherboard model, check BIOS download section. Release notes show version history, fixes, and improvements. Some BIOS interfaces display version history.
How do I enable Secure Boot for Windows 11?
Requirements: UEFI system, TPM 2.0 enabled. In BIOS: OS Type → Windows UEFI, Secure Boot → Enabled, Boot Mode → UEFI only. Clear secure boot keys if switching from Linux.
What are the risks of BIOS updates?
Main risks:
Power failure during update (bricking),
wrong BIOS file (permanent damage),
hardware incompatibility.
Mitigation:
Use UPS,
verify exact model,
backup working BIOS,
use manufacturer tools.
How do I password protect my BIOS?
Set Administrator/Supervisor password for BIOS access, User password for limited access, Power-on password for boot protection. Store passwords securely – BIOS password recovery often requires manufacturer support.
Can malware infect BIOS?
Yes, but rare. Modern threats: UEFI rootkits, firmware implants. Protection: Keep BIOS updated, enable Secure Boot, use reputable antivirus with UEFI scanning, avoid suspicious BIOS modifications.
How do I verify BIOS authenticity?
Download only from official manufacturer websites, verify digital signatures/checksums, use manufacturer’s update tools, avoid third-party BIOS repositories, check file properties for publisher information.
Does BIOS affect gaming performance?
Yes, significantly. Proper settings can improve: frame rates (5-15%), reduce input lag, enable hardware features (Resizable BAR), optimize memory speeds, enhance CPU boost behavior.
What BIOS settings affect boot time?
Fast Boot (enable),
Full Memory Test (disable),
Boot Delay (minimize),
Floppy Drive Detection (disable),
Network Boot (disable),
USB Detection (optimize),
POST screen timeout (reduce).
How do I optimize BIOS for SSD performance?
Enable:
AHCI mode,
TRIM support,
NCQ (Native Command Queuing).
Disable:
legacy IDE mode,
disk encryption (if not needed).
Configure:
proper SATA port (6Gbps),
power management settings.
Should I update BIOS for better RAM compatibility?
Yes, if experiencing stability issues or RAM not running at rated speeds. BIOS updates often include improved memory training algorithms, support for newer RAM modules, and better overclocking stability.
How do I reduce fan noise through BIOS?
Configure custom fan curves: lower RPM at idle temperatures, gradual ramp-up, higher temperatures before maximum speed. Enable: Smart fan control, PWM mode over DC mode, acoustic profiles.








What you’ve written here is not just a collection of words; it’s a thoughtful exploration of what it means to be human.
Thank you so much! I really appreciate your kind words 😊 I’m glad the post resonated with you—it truly means a lot!